4. CAN Usage
4.1 Introduction to CAN
The CAN protocol was developed by Bosch in the 1980s to meet the needs of the automotive industry. Over time, it has been widely adopted in other fields as well. CAN is a message-based communication protocol that allows multiple devices to communicate over a bus. Each device (node) can send messages to the bus, and all devices can receive these messages.
Key Features:
- Multi-master: CAN is a multi-master bus system where all nodes can initiate communication.
- Real-time capability: The CAN protocol is real-time, making it suitable for applications with high time sensitivity.
- Fault tolerance: CAN has strong error detection and fault tolerance, enabling it to function reliably in harsh environments.
- Priority: Message priority is determined by the message ID. The lower the ID, the higher the priority.
4.2 Example of Using CAN
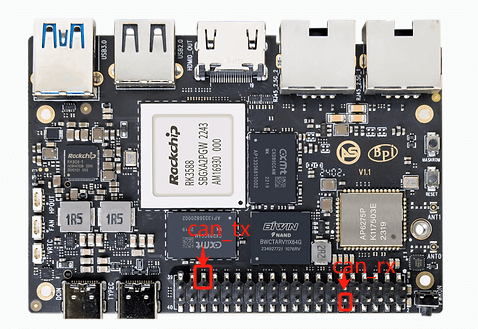
4.2.1 CAN Pins
For the ArmSoM-Sige7 example, CAN's position in the 40-pin header is as follows:
| Interface | Pin | Function |
|---|---|---|
| CAN1_TX_M1 | 3 | CAN1_M1 Data Transmission Pin |
| CAN1_RX_M1 | 5 | CAN1_M1 Data Reception Pin |
| CAN1_RX_M0 | 12 | CAN1_M0 Data Transmission Pin |
| CAN1_TX_M0 | 35 | CAN1_M0 Data Reception Pin |
4.2.2 Hardware Connections
Connections between CAN modules: CAN_TX connects to CAN_TX, and CAN_RX connects to CAN_RX.
4.2.3 Kernel Configuration
- rockchip_linux_defconfig configuration:
CONFIG_CAN=y
CONFIG_CAN_DEV=y
CONFIG_CAN_ROCKCHIP=y
CONFIG_CANFD_ROCKCHIP=y
- Kernel configuration:
cd kernel
make ARCH=arm64 menuconfig
make savedefconfig
- Choose:
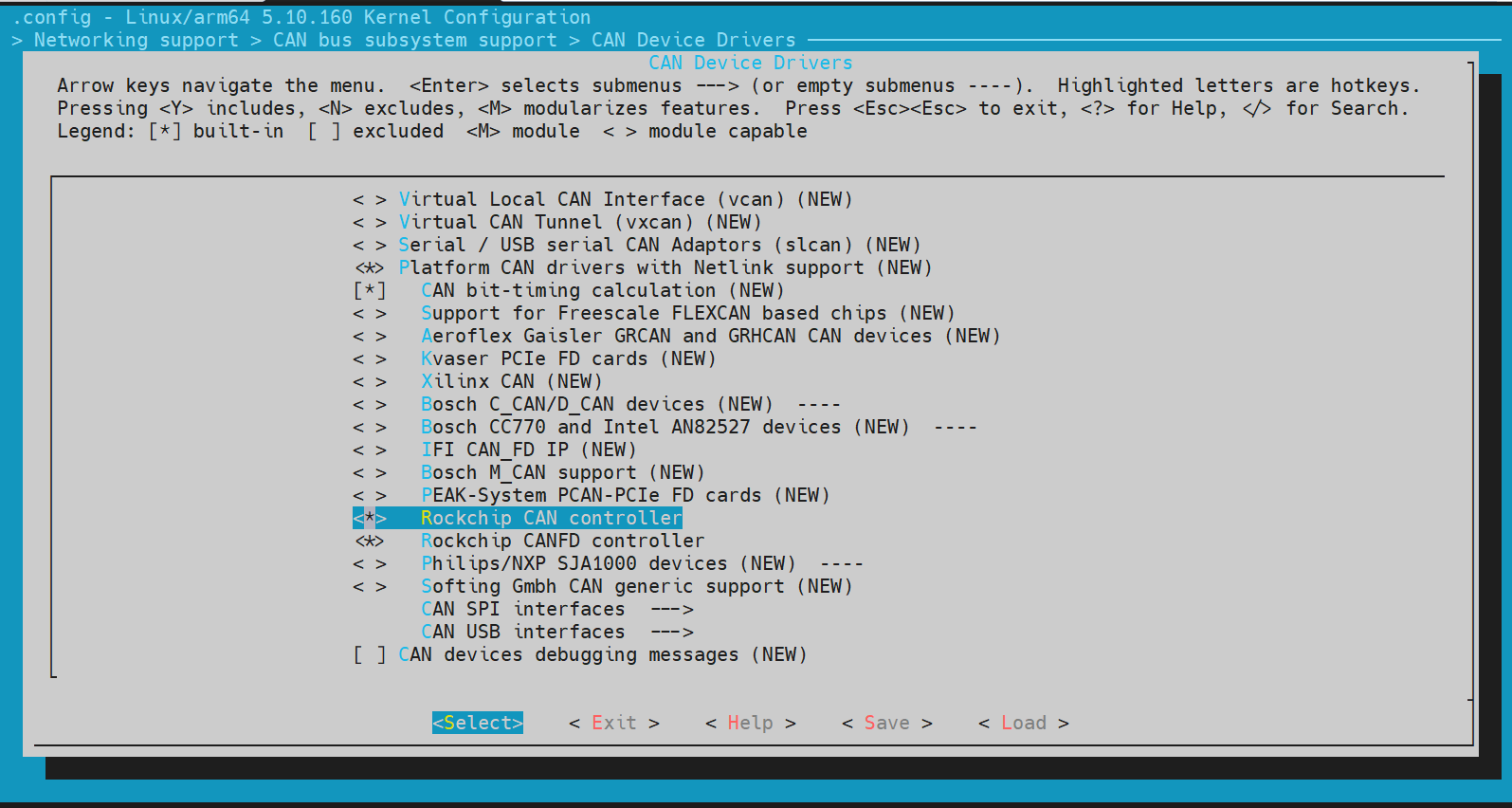
- Networking support → CAN bus subsystem support (
*) - CAN Device Drivers (
*) → Platform CAN drivers with Netlink support (*)
- Networking support → CAN bus subsystem support (
4.2.4 DTS Node Configuration
Main parameters:
- interrupts: Interrupt signal generated when a conversion is complete.
- clock: Clock properties used to drive the clock switch, and the reset property is used to reset the bus.
- pinctrl: Configures the CAN-related pin settings and function multiplexing.
/* can1 */
&can1 {
compatible = "rockchip,can-2.0";
reg = <0x0 0xfea60000 0x0 0x1000>;
interrupts = <GIC_SPI 342 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH>;
clocks = <&cru CLK_CAN1>, <&cru PCLK_CAN1>;
clock-names = "baudclk", "apb_pclk";
resets = <&cru SRST_CAN1>, <&cru SRST_P_CAN1>;
reset-names = "can", "can-apb";
tx-fifo-depth = <1>;
rx-fifo-depth = <6>;
status = "okay";
assigned-clocks = <&cru CLK_CAN1>;
assigned-clock-rates = <200000000>;
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&can1m0_pins>; // Configured according to the schematic
};
compatible = "rockchip,can-1.0"is used to match the CAN controller driver.compatible = "rockchip,can-2.0"is used to match the CANFD controller driver.assigned-clock-ratesis used to configure the CAN clock rate. If the CAN bitrate is below or equal to 3 Mbps, it is recommended to set the CAN clock to 100 MHz for more stable signals. For bitrates higher than 3 Mbps, a 200 MHz clock is sufficient.- pinctrl configuration: According to the actual board layout, configure the
can_handcan_lpins for the CAN functionality.
4.2.5 Enabling CAN Communication Interface
By default, the CAN interface is disabled, and it needs to be enabled for use.
In the Ubuntu/debian operating system, the/boot/uEnv/uEnv. txt file is used to configure system startup parameters and device tree plugins. You can enable or disable the CAN device tree overlay by editing this file to ensure that the CAN bus is correctly loaded at boot time.
To check or enable the CAN-related device tree overlays, follow these steps:
View Device Tree Overlay Configuration: Open file: Open the/boot/uEnv/uEnv. txt file through the terminal.
To enable the rk3588-can1-m1, add the following line (as an example):
dtoverlay=/dtb/overlay/rk3588-armsom-can1-m1.dtbo
#dtoverlay=/dtb/overlay/rk3588-armsom-i2c0-m1.dtbo
Remove the # before dtoverlay, after editing, save the file and exit the editor to restart the system for the configuration to take effect:
armsom@armsom:/boot$ sudo vi /boot/uEnv/uEnvarmsom-sige7.txt
cmdline="earlyprintk console=ttyFIQ0 console=tty1 consoleblank=0 loglevel=7 roott
wait rw rootfstype=ext4"
enable_uboot_overlays=1
#overlay_start
#40pin
#dtoverlay=/dtb/overlay/rk3588-armsom-can1-m0.dtbo
dtoverlay=/dtb/overlay/rk3588-armsom-can1-m1.dtbo
#dtoverlay=/dtb/overlay/rk3588-armsom-i2c0-m1.dtbo
#dtoverlay=/dtb/overlay/rk3588-armsom-i2c1-m0.dtbo
#dtoverlay=/dtb/overlay/rk3588-armsom-i2c3-m1.dtbo
#dtoverlay=/dtb/overlay/rk3588-armsom-i2c7-m3.dtbo
#dtoverlay=/dtb/overlay/rk3588-armsom-i2c8-m4.dtbo
#dtoverlay=/dtb/overlay/rk3588-armsom-pwm2-m1.dtbo
#dtoverlay=/dtb/overlay/rk3588-armsom-pwm3-m1.dtbo
#dtoverlay=/dtb/overlay/rk3588-armsom-pwm5-m2.dtbo
#dtoverlay=/dtb/overlay/rk3588-armsom-pwm6-m2.dtbo
#dtoverlay=/dtb/overlay/rk3588-armsom-pwm7-m3.dtbo
#dtoverlay=/dtb/overlay/rk3588-armsom-pwm8-m0.dtbo
#dtoverlay=/dtb/overlay/rk3588-armsom-pwm12-m0.dtbo
#dtoverlay=/dtb/overlay/rk3588-armsom-pwm13-m0.dtbo
#dtoverlay=/dtb/overlay/rk3588-armsom-pwm13-m2.dtbo
After executing the above modifications, restart the system
armsom@armsom:/boot$ sync
armsom@armsom:/boot$ sudo reboot
- Q: If the system is rebooted by directly pulling the power, is it possible that files are not updated or the overlay system fails to start?
- A: When you abruptly disconnect the power or force a shutdown, there is a risk that files may not be properly synchronized from memory (RAM) to the storage device (e.g., hard drive or SSD). This happens because the operating system typically caches data in memory and writes it to the disk periodically. To avoid this issue, it is recommended to run the "sync" command before shutting down, ensuring that all data is written to the disk before pulling the power or shutting down.
4.3 CAN Communication Testing
- Check current network devices:
ifconfig -a
- Start CAN:
ip link set can0 down # Disable CAN interface
ip link set can0 type can bitrate 500000 # Set bitrate to 500 Kbps
ip -details -statistics link show can0 # Show can0 details
ip link set can0 up # Enable CAN interface
- Send CAN Messages:
cansend can0 123#DEADBEEF # Send (Standard Frame, Data Frame, ID: 123, Data: DEADBEEF)
cansend can0 123#R # Send (Standard Frame, Remote Frame, ID: 123)
cansend can0 00000123#12345678 # Send (Extended Frame, Data Frame, ID: 00000123, Data: DEADBEEF)
cansend can0 00000123#R # Send (Extended Frame, Remote Frame, ID: 00000123)
- Receive CAN Messages:
candump can0 # Dump CAN messages from can0